Question #c6802
1 Answer
Aug 26, 2017
option(B) yields an optically active product upon reduction of
Explanation:
Chiral molecules have no line of symmetry and this makes them optically active.When you look at the molecules before the reaction they all are asymmetric and they are optically active.
A) D-ribose
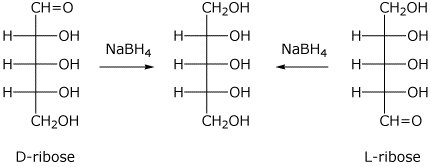
I didn't get an image with only D-ribose
There is a line of symmetry in this aditol, therefore it is achiral and not optically active
(B) L-lyxose
The product is chiral and optically active
(C)L-xylose

There is a line of symmetry and this aditol is achiral
(D)D-xylose


There is a line of symmetry and this aditol is achiral
In the last 2 options I have used the same image because the configuration of aldehyde group is not the same in both the aldopentose.

