Question #b585f
2 Answers
Please refer to the explanation.
Explanation:
I will try to list its most important points here. For more information, visit: https://www.thoughtco.com/animal-anatomy-epithelial-tissue-373206.
There are many types of epithelial tissues, and here are some of them:
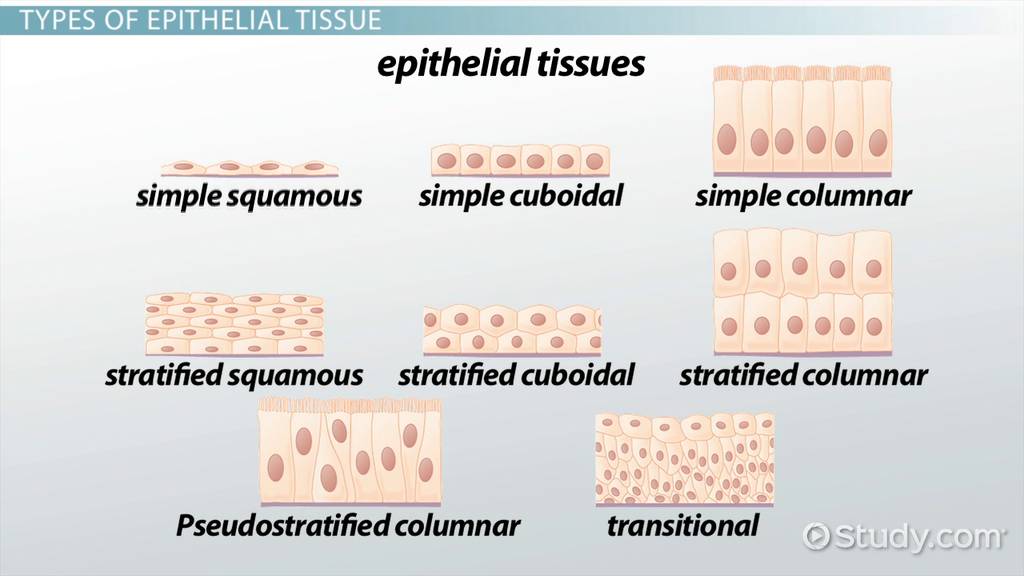
Well, these tissues are made of epithelial cells, which are really important for animals.
First, they are the cover for the outside skin of the animal. They cover and line the organs, blood vessels, and body cavities.
The epithelial cells combine together and form a thin layer called the endothelium. This part covers the brain, skin, lungs, and the heart.
The epithelial tissue also protects the skin against microorganisms, and therefore acting like a membrane. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms have to pass this layer before reaching other layers of the skin.
Another function of this tissue is to absorb nutrients and excrete substances. During digestion, these tissues absorb the nutrients in an organ, such as the small intestine.
In other glands, these tissues excrete hormones, enzymes, and other compounds. In kidneys, they excrete out waste. In sweat glands, they excrete out perspiration (sweat).
I hope that helps!
See Below.
Explanation:
I recommend seeing this webpage for the details I miss out.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epithelium
->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->->
Epithelial Tissues are on of the four basic types of animal
tissues. They line the cavities and surfaces of blood vessels and organs throughout the body.
Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium can be classified into two types.
i) Simple Epithelium :- It is only one-layered.
It is further classified into four types.
a) Simple Squamous Epithelium :- Helps in diffusion and
exchange of gases. Found in alveoli, skin, walls of capillaries.
b) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium :- Found in Kidney, Salivary
Glands, Pancreas. They may be secretory, absorptive or excretory.
c) Simple Columnar Epithelium :- Secretory, absorptive or
excretory; They can be cilliated or non-cilliated. Cilliated
ones are found in female reproductive tract and uterus. Non-cilliated ones are found in Small Intestine, can contain microvilli.
d) Psuedostratified Columnar Epithelium :- This can also be
cilliated or non-cilliated. Cilliated ones are found in
respiratory tract, that's why it is specially called respiratory
epithelium.
ii) Stratified Epithelium :- Multilayered Epithelium.
It is divided into three types by the specialisations., and every type is divided
into squamous, cuboidal and columnar type.
a) Keratinized Epithelium :- Present in Mammalian Skin, The Keratin Layer makes it waterproof. In case of Non-Keratinised, the lining of oesophagus is an example.
b) Parakeratinized Epithelium :- Keratin Layer is there, but the apical cells retain their nuclei, unlike Keratinized Epithelium.
c) Transitional Epithelium :- As the name suggests, it can have dual characteristics. It appears as cuboidal while non-stretched; and squamous while streched. It is also called Urothelium as it specially occurs in urinary bladder, ureter and urethra.
Broadly, Epithelium also helps in immunity, as it prevents bacteria, viruses and other microbes to invade body.
Hope this helps.


