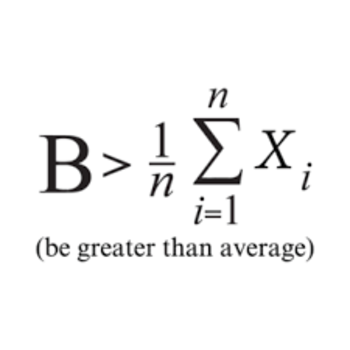Why is the change in Gibbs energy negative?
1 Answer
Well, it is not always negative...
Explanation:
If the change in Gibbs free energy,
The majority of reactions studied in laboratories are often spontaneous at room temperature- so it might seem that the majority of reactions has a value for Gibbs free energy which is negative, but this is not necessarily true.
The change in Gibbs free energy is given at constant temperature as:
#DeltaG=DeltaH-TDeltaS#
For a given reaction with given constant temperature
From this, it can be established that reactions which have a positive
However, reactions with a negative
Other combinations of