What is the function of a nephridia in an earth worm?
1 Answer
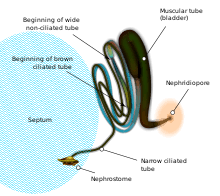
Nephridia are segmentally arranged coiled tubules which act as excretory organs in the earthworm.
Explanation:
They are primarily units of excretory system and the type of nephridia found in earthworms are called metanephridia.
These ciliated tubules pump surplus ions, metabolic wastes, toxins, and useless hormones (all dissolved in water) out of the organism by directing them down funnel shaped bodies called nephrostomes. As the metabolic wastes move through the body cavity, the cilia absorbs the cavity fluid while specialised tubule cells absorb any useful nutrients that remain in the waste.
The primary urine produced by filteration of circulating fluid (blood) is converted into secondary urine through selective reabsorption by the cells lining the metanephridium. Once the wastes that are filtered out have been fully processed through the body cavity, what remains is passed out of the earthworm's body through a structure called the nephridiopore.

 )
) 