What are intermolecular forces?
1 Answer
They are dipole-dipole forces, hydrogen bonds, and London dispersion forces.
Explanation:
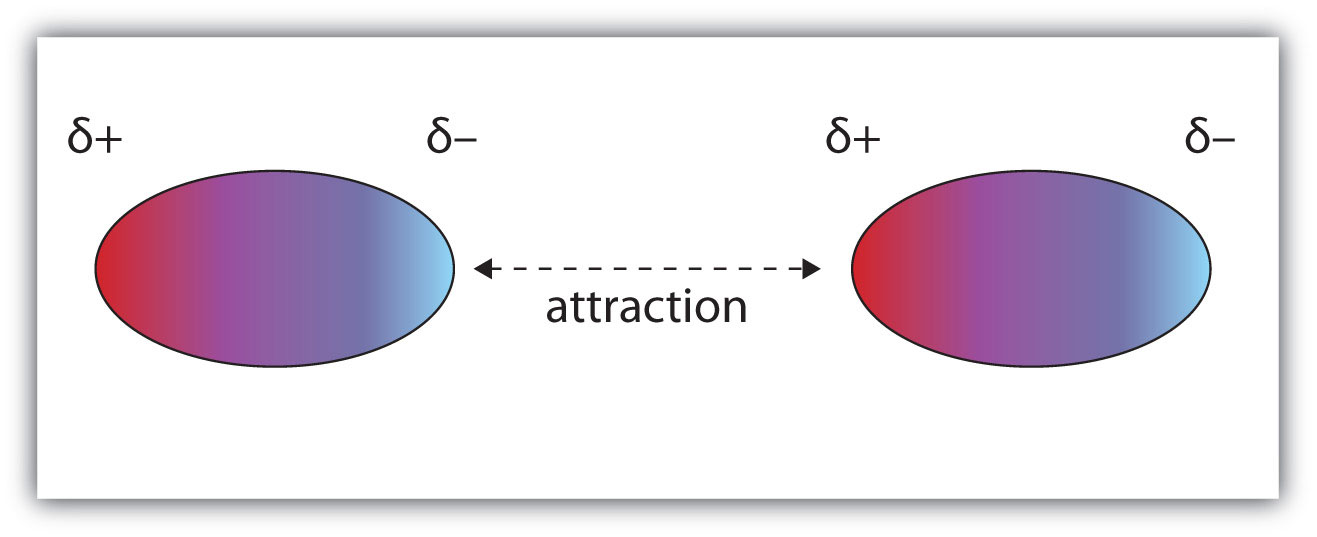
DIPOLE-DIPOLE FORCES
Two nearby polar molecules arrange themselves so that the negative and positive ends line up. An attractive force holds the two molecules together
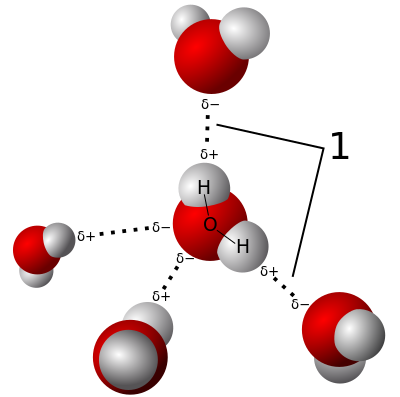
HYDROGEN BONDS
The H atom in an O-H, N-H, or F-H bond has a partial positive charge. The N, O, or F atoms in a neighbouring molecule have a partial positive charge.
The dipole-dipole attractions between these charges are hydrogen bonds. Water molecules have strong H-bonds.
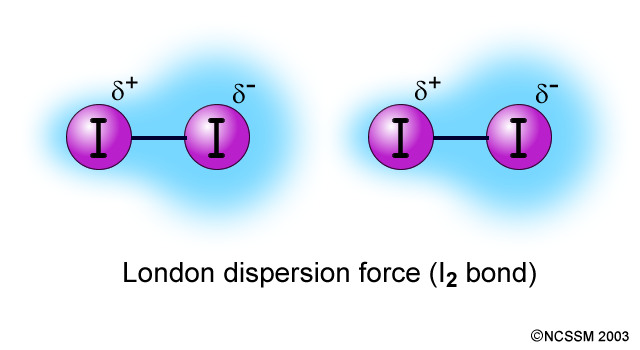
LONDON DISPERSION FORCES
At any given instant, there may be a greater electron density on one end of a nonpolar molecule than on the other. This instantaneous dipole can induce a dipole in a neighbouring molecule. This causes a weak attractive force called a London Dispersion Force.