Question #3e390
1 Answer
Feb 13, 2016
A conjugated carbonyl group has a
Explanation:
Examples of unconjugated carbonyl compounds are propanal and propanone.
Typical conjugated (or α,β-unsaturated) carbonyl compounds are propenal

and
butenone
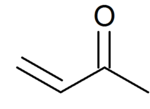
In addition to a normal

It can be attacked by nucleophiles at either the β-carbon or the carbonyl carbon.

Note that the product of 1,4-addition is an enol that will tautomerize to the more stable carbonyl compound.

