Question #30e65
1 Answer
May 14, 2017
X-ray diffraction or X-ray crystallography is a technique used to study and determine the structure of a crystal at atomic or molecular level.
In this process atoms of crystals diffract an incident X-Ray beam in specific directions.
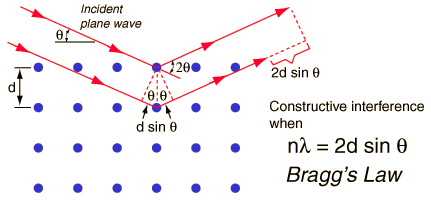
Bragg's Law.
Maximum in the observed intensity of X-rays occurs as per the following conditions
- The angle of incidence
#=# angle of scattering. - The difference in pathlength is equal to integeral multiple of wavelength
#lambda# of X-rays.
#" "2dsintheta=nlambda#
