Anaerobic respiration occurs in muscle cells in the absence of oxygen.
![enter image source here]()
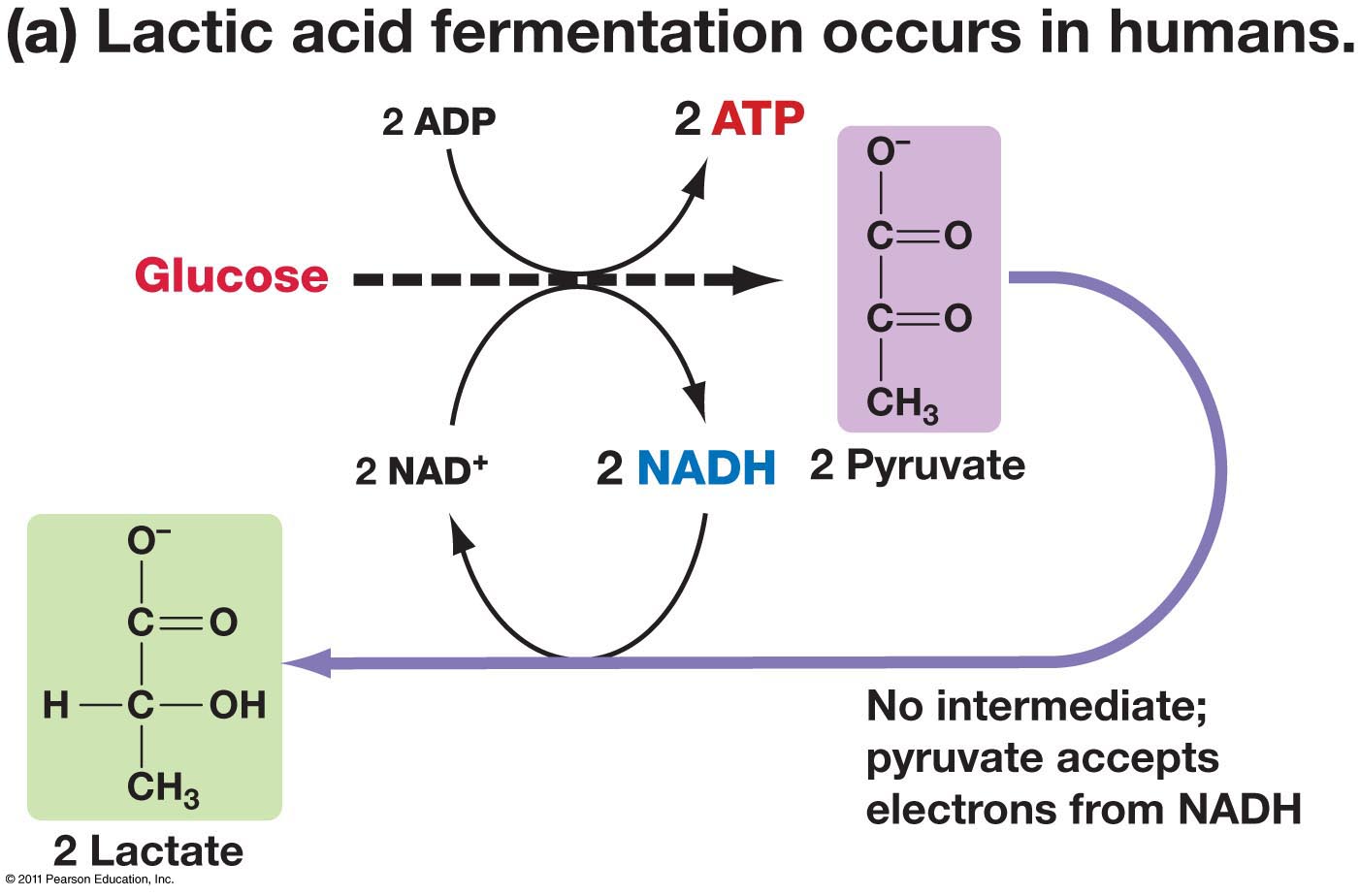
When you exercise and your muscles are not getting the oxygen they need, they resort to undergoing lactic acid fermentation . This reaction generates #2 "NAD+"# molecules for every 2 pyruvate molecules with the help of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase .
This reaction is important because the #2 "NAD+"# that are regenerated allows glycolysis to continue so that it may produce 2 net ATP molecules which can be used to provide the energy for the muscle cells.
Yeast cells undergo fermentation as well but the process produces a different end product, ethanol, via a 2 step process.
![enter image source here]()
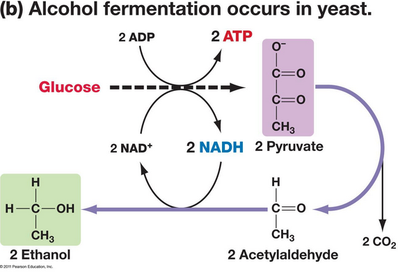
As you can see, #"pyruvate"# will be decarboxylated to become #"acetaldehyde"#. Decarboxylation just means a molecule will lose a #CO_2# group. The enzyme that helps with the process is called pyruvate decarboyxlase.
#"Acetaldehyde"# is then reduced to #"ethanol"# with the help of alcohol dehydrogenase.
Now a little bit of organic chemistry will help you. We know that #"acetaldehyde"# is reduced to #"ethanol"# because the carbonyl group disappears and an alcohol appears. Reduction cannot occur without something else being oxidized. What was oxidized? The #NADH# molecule from glycolysis becomes oxidized to become #NAD+#. Again, the #"NAD+"# molecules regenerated will be used back up again for glycolysis, continuing the cycle.



