A particle of mass m strikes a wall at an angle of incidence 60° with velocity V elastically. Then the change in momentum is?
1 Answer
Apr 18, 2018
Explanation:
Check what is meant by "incident" angle. See drawing for one interpretation. Swap 30 for 60 if it's the optics definition.
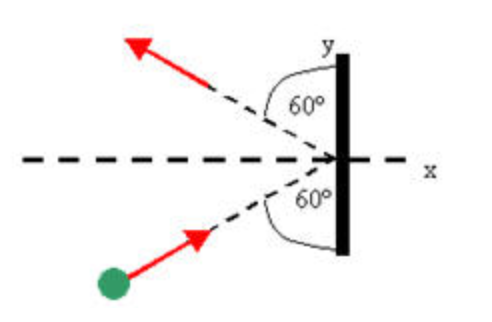
For an elastic collision we can say that:
#mathbf p_i = mV(( sin 60),(cos 60))#
and
#mathbf p_f = mV(( -sin 60),(cos 60))#
So, kinetic energy is preserved because

