How do nucleic acids function?
1 Answer
Nucleic acids are biological macromolecules composed of nucleotide monomers. Nucleic acid forms the genes and also helps in gene expression.
Explanation:
There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA
DNA contains the genetic information of an organism. It also gets inherited from one generation to the next, and along with it the genes are passed on to progeny.
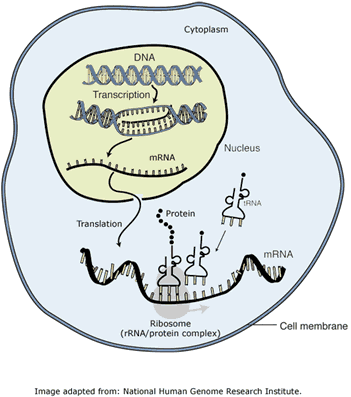
The information stored in DNA is decoded into particular amino acid sequences of proteins; these proteins are essential to carry out numerous functions of the cell. This conversion of genetic recipe into protein is aided by different RNA molecules.
Hence, the amino acid sequence of proteins is determined by the nucleotide sequence of both DNA and RNA molecules. RNA carrying genetic code for protein synthesis is called messenger RNA. There are two more types: tRNA and rRNA.

( )
)
rRNAs are integrated parts of ribosomal particles. tRNAs collect the amino acids from cytoplasmic pool and bring them on ribosomes to become aligned along mRNA.
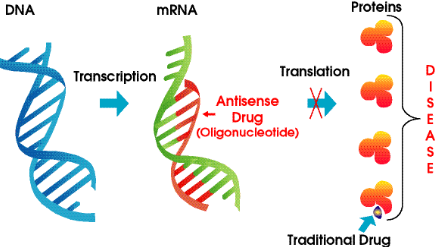
Then there are ribonucleic acids known as antisense RNA. These molecules are able to silence mRNA, that is antisense RNA are involved in post-transcriptional gene silencing.
( )
)

