How does acid rain form?
2 Answers
Acid rain forms when water reacts with sulfur dioxide or nitrogen dioxide.
Explanation:
Acid rain forms when water molecules in the atmosphere react with sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides to form an acidic compound. The resulting compound has a lower pH.
 )
)
The chemical reactions that occur when water molecules mix with sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are below:
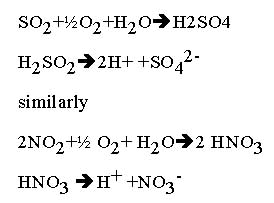
Nitrogen oxides can be produced naturally by lightening strikes and sulfur dioxides is formed when volcanoes explode, but acid rain can also be caused by emissions due to humans.
Sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides reacting with water.
Explanation:
SULFUR OXIDES
1) Sulfur dioxide
#"S"(s) + "O"_2(g) -> "SO"_2(g)#
2) Sulfur dioxide
#2"SO"_2(g) + "O"_2(g) -> 2"SO"_3(g)#
3) The oxides react with water to form acids
#"SO"_2(g) + "H"_2"O"(l) -> "H"_2"SO"_3(aq)#
#"SO"_3(g) + "H"_2"O" (l) -> "H"_2"SO"_4(aq)#
NITROGEN OXIDES
1) Nitrogen monoxide
#"N"_2(g) + "O"_2(g) -> 2"NO"(g)#
2) Nitrogen monoxide
#2"NO"(g) + "O"_2(g) -> 2"NO"_2(g)#
3) Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to form nitric acid
#2"NO"_2(g) + "H"_2"O"(l) -> "HNO"_3(aq) + "HNO"_2(aq)#
or it reacts with oxygen and water and becomes nitric acid
#4"NO"2_(g) + "O"_2(g) + "H"_2"O"(l) -> 4"HNO"_3(aq)#
The above was taken from Oxford IB Chemistry Study Guide by Geoffrey Neuss textbook (pg 62)
 )
)