How does divergent evolution differ from convergent evolution?
1 Answer
Apr 21, 2017
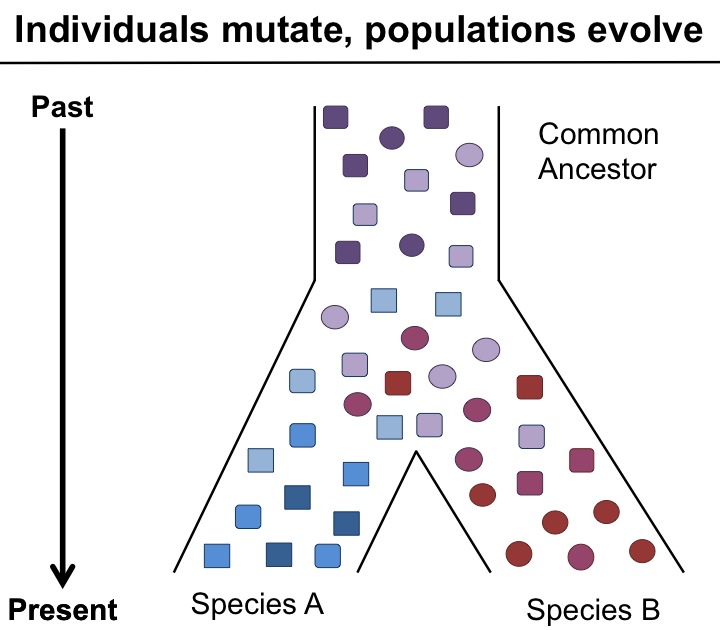
Generally evolution is divergent: I say so because that is how this earth has today become home to immensely diverse kinds of life.
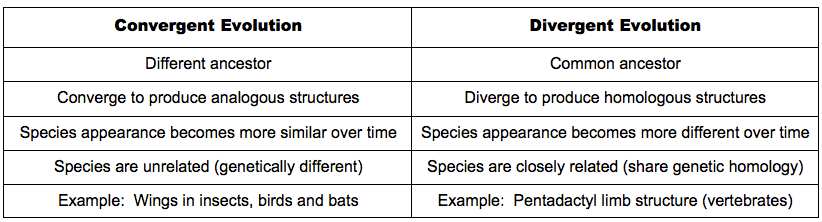
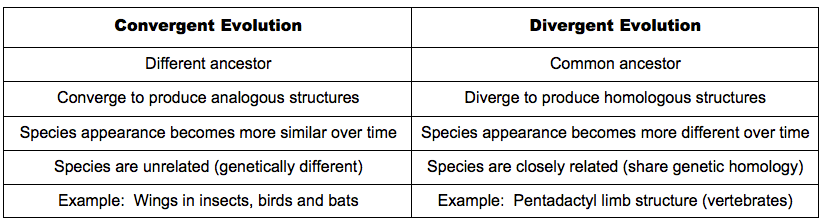
- Divergent evolution simply means appearance of more than one descendant species from an ancestral species population. Mammalian forelimbs, for example, follow an ancestral pentadactyl limb plan but work very differently in different orders.
- Divergent evolution may lead to appearance of homologous organs. Divergence appears due to adaptation of related organisms in different environmental conditions and habit.
( )
)
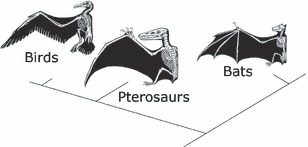
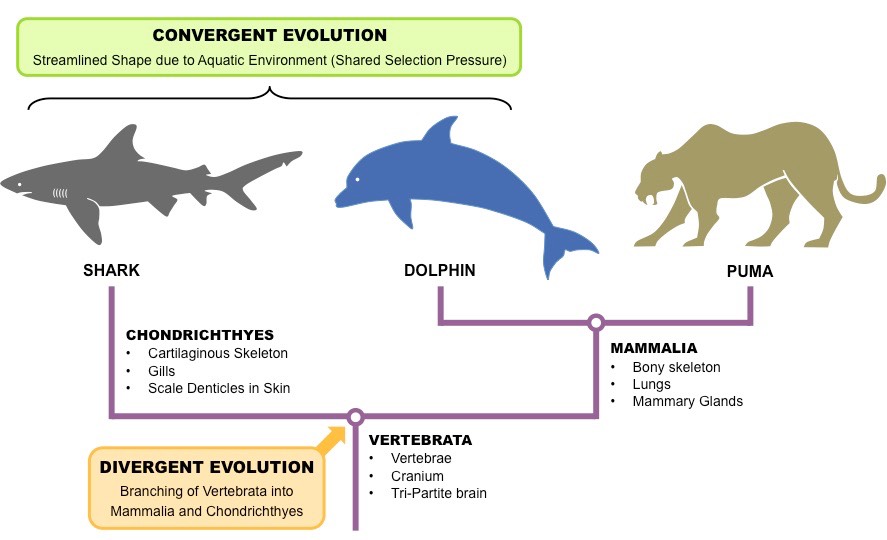
- We also find organisms which evolved superficial/plastic similarity in appearance or similar adaptations in habit to other organisms, with which they are not closely related. This is convergent evolution as exhibited by shark and dolphin: they belong to different vertebrate class but both are adapted to aquatic life.
- Convergent evolution leads to appearance of analogous organs where infrastructure of such organs may differ but the functional achievement remains same. This is because of the fact that similarity in appearance and behaviour evolves due to similar environmental pressure.

( )
)
( )
)

( )
)
