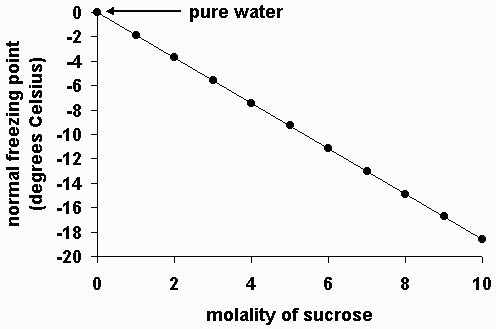
How does molality affect the freezing point?
1 Answer
May 12, 2014
Higher molality means a lower freezing point!
Explanation:
Freezing point depression is an example of a colligative property. The more concentrated a solution, the more the freezing point of water will be depressed.
The solute particles basically interfere with the ability of the water molecules to freeze because they get in the way and make it more difficult for the water to hydrogen bond.
Here is a video which illustrates how to calculate the freezing point depression of water for 1molal solutions of sugar and NaCl.