How does the autonomic nervous system function in the maintenance of homeostasis?
1 Answer
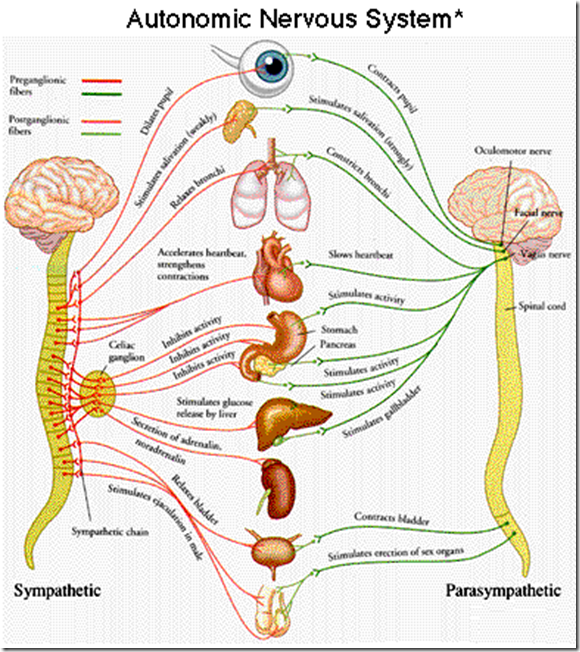
Autonomic nervous system (ANS) is made of motor nerves travelling from CNS to PNS. All actions of ANS are involuntary and help in maintaining a stable internal physiological state. 
Explanation:
Autonomic nevous system has two distinct outlets: sympathetic and parasympathetic. First is primarily responsible for adjusting our body to stress while the latter is responsible for slowing down the physiology. Thus sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of ANS are antagonistic systems working together to maintain internal balance of the body.
A very short list of their functions could be like following:
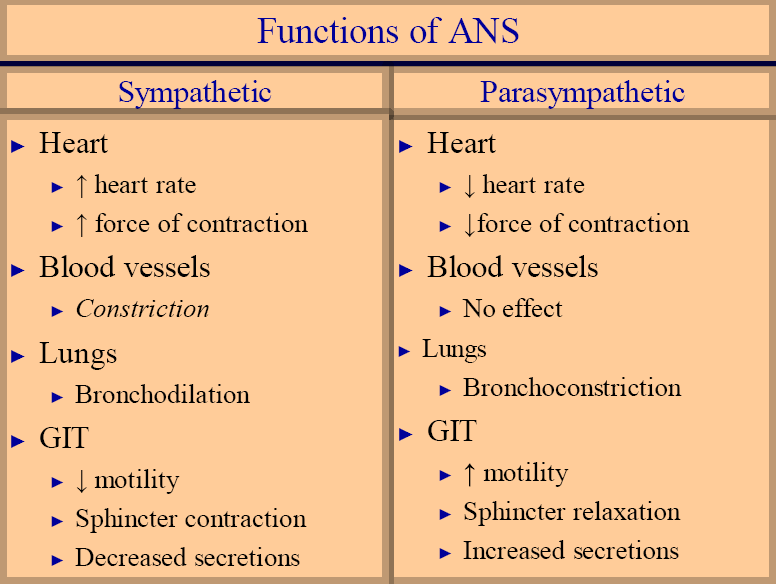
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems arise from CNS and terminate in designated organs or tissues. Axonic ends of neurons secrete different neurohumor substances and accordingly excitatory or inhibitory signals are delivered to the organs.
Each organ receives both sympathetic and parasympathetic connections, hence its function could be modified depending on activity levels or physiological demands, and a stable state could always be restored.