How would you find the area of an equilateral triangle using the Pythagorean Theorem?
1 Answer
Dec 1, 2015
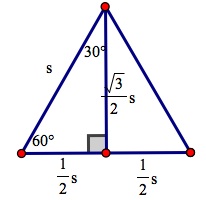
We can see that if we split an equilateral triangle in half, we are left with two congruent equilateral triangles. Thus, one of the legs of the triangle is
If we want to find the height, we use the Pythagorean Theorem:
If we want to determine the area of the entire triangle, we know that

