What are some examples of wave-particle duality?
1 Answer
Wave–particle duality means that every elementary particle exhibits the properties of both particles and waves.
The wave-like nature of light explains most of its properties.

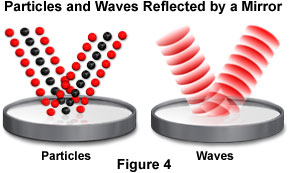
Reflection
Reflection is the change in direction of a wave or a particle when it hits a surface.
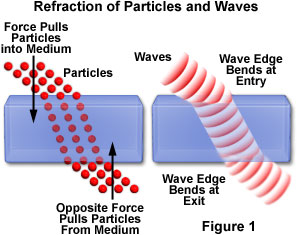
Refraction
Refraction is the bending of a wave as it passes from one medium to another.
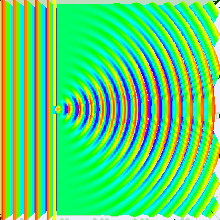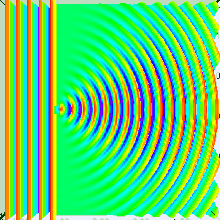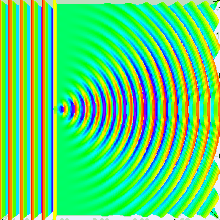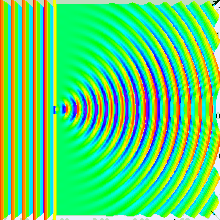
Diffraction
Diffraction is the bending of a light wave as it passes around the edge of an object.
Interference
Interference is the combination of two sets of waves to produce a resultant wave. Waves that are out of phase will cancel each other and produce dark areas.

Polarization
Polarization is the forcing of light waves to vibrate in a single plane.

Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when light shines on metals. In this effect, the light behaves as a stream of particles.


