What is a major resonance contributor?
1 Answer
A major resonance contributor is one that has the lowest energy.
We can often write more than one Lewis structure for a molecule, differing only in the positions of the electrons.
Each individual structure is called a resonance contributor.
The most stable structures contribute most to the resonance hybrid. They are called the major resonance contributors.
In order of importance, a major contributor must have:
- The most atoms with complete octets.
- Any formal charges on the atoms most able to accommodate them.
- The most covalent bonds.
- The smallest number of formal charges.
Example 1
You can write three possible Lewis structures for formaldehyde, H₂CO:
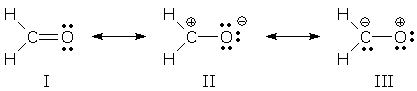
The lowest energy form is I, because every atom has a complete octet. It is the major contributor.
II is lower in energy than III, because the negative charge is in the more electronegative O atom.
The major contributor is I.
Example 2
You can write two structures for the conjugate acid of formaldehyde.

The first structure is the major contributor, because every atom has a complete octet. This is despite the fact that the positive charge is on the more electronegative O atom.
Example 3
We can write two contributors for the conjugate base of acetone.
All atoms in C and D have a complete octet. But D has the negative charge on O, so D is the major contributor.

