What is the difference between condensation polymerization and addition polymerization?
1 Answer
Consider the following explanation.
Explanation:
Addition Polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of alkene monomers to produce a single huge molecule only.
Note:Nothing is eliminated, the monomers simply add up to each other.
Such reactions are catalyzed typically by peroxides and acids at a pressure of about
Typical examples are the formation of Polyethylene from Ethylene or the formation of PolyVinyl Chloride (PVC) from Vinyl Chloride.
The reaction in the case of polyethylene comes out to be:
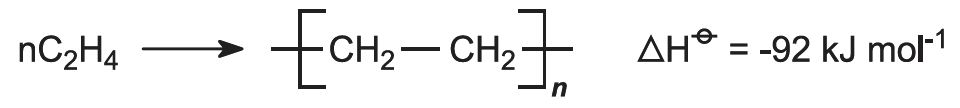 (Site Used for Image Source only)
Condensation Polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like
Typical examples of such polymers are Polyesters and Polyamides.
Nylon,6-6 is the most common polyamide which is obtained by heating hexamethylene diamine with adipic acid under
The reaction comes out to be:
 ) (Site used for Image Source Only)
) (Site used for Image Source Only)

