What is the relationship between having full valence shells and formal charges?
1 Answer
The formal charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons "belonging" to the bonded atom and those in the full valence shell.
A quick formula for calculating the formal charge (FC) is
FC = V – L – B, where
V = number of valence electrons in isolated atom
L = number of lone-pair electrons
B = number of bonds
1. Let's apply this to the boron atom in BH₄⁻.

V = 3; L = 0; B = 4.
So FC = 3 – 0 – 4 = -1
B has a formal charge of -1 even though it has a full valence shell.
2. What about the C atom in CH₄?
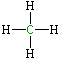
V = 4; L = 0; B = 4.
So FC = 4 – 0 – 4 = 0
Here C has a full valence shell and a formal charge of 0.
3. Now look at the hydronium ion.

V = 6; L = 2; B = 3.
So FC = 6 – 2 – 3 = +1.
O has a full valence shell and a formal charge of +1.
In each case, the atom has a full valence shell but the formal charge can be negative, zero, or positive.

