What tool is used to measure gas pressure?
1 Answer
The device you use to measure gas pressure depends on the pressure you wish to measure.
Explanation:
The most common devices are listed below.
PRESSURE GAUGE
One method of measuring higher pressures is to use a pressure gauge. The pressure-sensing element may be a tube, a diaphragm, a capsule, or a set of bellows that change shape in response to the gas pressure. The deflection of the pressure-sensing element is read by a linkage connected to a needle. Typical pressure ranges go from 0-1 bar up to 0-600 bar.

ANEROID BAROMETER
An aneroid barometer is a pressure gauge that is calibrated to measure pressures in the approximate range from 950 to 1070 mbar. If you needed to know the atmospheric pressure for a laboratory experiment, you or your instructor probably got it from an aneroid barometer.

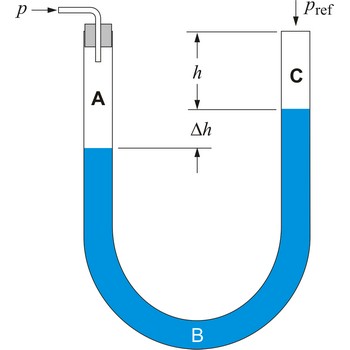
U-TUBE MANOMETER
A simple device to measure gas pressure is a U-tube manometer. It usually contains water or mercury in a U-shaped tube. One end of the U tube is exposed to the unknown pressure, and the other end is open to the atmosphere.
The pressure of the gas is represented by the difference in heights between the two levels Δh and is measured by a calibrated scale placed behind the liquid columns. You have probably used a device like this in the lab as well.
VACUUM GAUGE
A vacuum gauge is similar to a pressure gauge. Common gauges measure pressures from 1000 mbar to about 50 mbar. However, some specialized devices measure pressures down to 10⁻¹⁴ bar.
(From Actrol)
McLEOD GAUGE
A McLeod gauge isolates a sample of gas and compresses it in a modified mercury manometer until the pressure is a few millibars. Its useful range is from 100 nbar to 1 nbar.


