Energy in Metabolic Pathways
Key Questions
-
Answer:
they use the stored energy.
Explanation:
there are three ways (of which i know this is not an exhaustive list ) in which the energy is stored
ATP stored in phosphate group
GTP stored in phosphate group
NADH/FAD stored in by getting oxidizedthese molecules are used during various process. what is interesting to know is that when cell require energy they use these molecules to extract the energy stored in them.
the choice of using them in the cell is dependent on the amount of energy required by the cell.
ATP upon hydrolysis yield around 7kcal/mol of energy which is quiet high required for movement of muscle fibers
GTP is a low energy yielding molecule.
NADH/FAD are used in various reaction of citric acid cycle.
below is a figure gives examples of ATP and NADH/FAD usage.
source: online.science.psu.edu/sites/default/files/biol011/Fig-23-Chemical-Krebs.gi f source : http://www.chemistryexplained.com/images/chfa_02_img0372.j pg

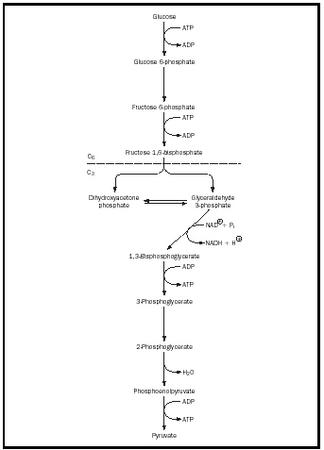
Figures explain usage of NAD , FAD and ATP
source
-
Answer:
Agree and added a little
Explanation:
I totally agree with him..we could use GTP too..and muscle for energy burst out could use creatinine phosphate ..check that awesomeness :)
-
One metabolic pathway is expressed this way:
LIGHT (energy) plus#CO_2# +#H_2O# ----> (glucose)You will find this reaction in plants and algae (and some bacteria). They take sunlight and combine carbon dioxide and water. Then they create glucose and oxygen gas. Chemists say they are fixing the atmospheric carbon (C).
Remember, plants put the energy into glucose. Glucose is in most of the food you eat and the oxygen you breathe come from these plants. Even if you have a piece of meat, that animal was originally able to get its' glucose from plants.
Cellular respiration is a 3 step process that includes glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and a number of electrons being pushed across the membrane of the mitochondria. Together they take that energy out of the sugar related molecules.
Glucose is then combined with oxygen and releases usable energy, carbon dioxide, and water:#C_6H_12O_6# +#0_2# ----> usable energy (ATP) plus#CO_2# Using glucose to create energy, cells can use that extra energy to power their functions.
The energy is not just floating around but it is stored in an excitable compound called ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
ATP is the power molecule used by all cells to power the secondary reactions to keep you alive. The#C0_2# that we produced from the breakdown of glucose in our mitochondria is exhaled when we breathe.Plants then can take that carbon dioxide and use it to make sugars, completing a cycle.