Regulatory DNA / RNA / RNAi
Key Questions
-
Answer:
RNAi (RNA interference) is a process dominated by small RNA which effect the gene expression at post transcription level.
Explanation:
RNAi is dominated by small RNA like (shRNA and miRNA), these RNA are synthesized inside the cell as well as can be introduced out from the cell.
what these small RNA does is they form a RISC complex which then goes and binds to various target mRNA which have complementarity to them and then employ two different strategies
- stop the translation
- tag the mRNA for degradation by endonucleases.
through these two strategies small RNA interfere with the gene expression in the cell.
below video is a good way to understand whole concept. WATCH THIS VIDEO
-
Answer:
rnai
Explanation:
rnai is a defensive mechanism of the body which destroys the double stranded rna produced in the body
ex. Meloidogyne incognitia which affects the roots of Tobacco plant is destroyed by this rnai technique -
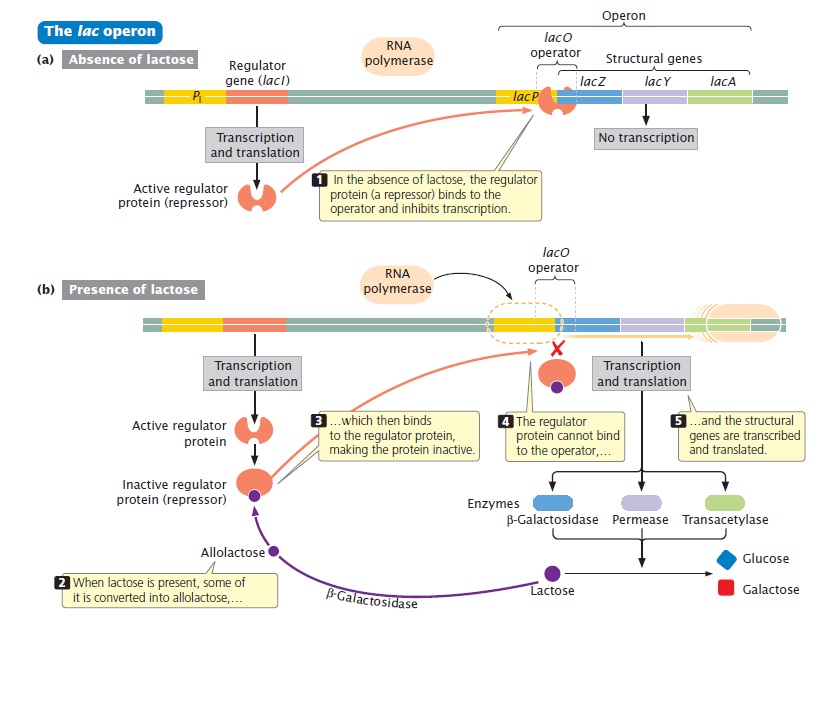
A great example I know is the lac operon located in prokaryotic DNA that dictates whether bacteria in the lower GI tract use lactose or glucose for energy.

The lacI area of the DNA constitutively expresses a repressor molecule that negatively controls lacZ and lacY expression by blocking RNA primase from synthesizing RNA in order to break down galactose.
When there is high levels of extracellular glucose, galactoside permease is inhibited from letting the cell membrane from being permeable to lactose.
However, when extracellular glucose levels are low, the cell membrane may be more permeable to lactose, which induces transcription of the lacY and lacZ genes to be expressed into proteins and enzymes that promote lactose metabolism.
Moreover when a cAMP-CAP complex is formed within the cell as a result of intercellular lactose, it promotes transcription of the aforementioned genes.
Here's another figure explaining what I just said: