Question #72d37
2 Answers
Lipids are organic compounds such as fat or oil.
Explanation:
Organisms uses lipids to store energy. There are two types of lipids,
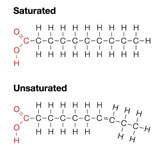
- Saturated Fatty Acids
This is used by animals to store fats. The structure of this is that carbon atoms are bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible.
- Unsaturated Fatty Acids
This is used by plants to store energy. Molecules in this lipid are bonded to other group of atoms rather than hydrogen atoms.
The basic structure of lipids is that they all have a polar head and a nonpolar tail.
Explanation:
Lipids are defined by their solubilities, so they have varying structures, but they all have one thing in common: a polar, hydrophilic "head" and a nonpolar, hydrophobic, hydrocarbon "tail".
Lipids include the following classes.
Fats
Fats are esters of glycerol with long-chain fatty acids.

The ester groups form the polar head of the molecule.
Phospholipids
In phospholipids, one of the fatty acids has been replaced by a phosphate group and a simple molecule such as choline.

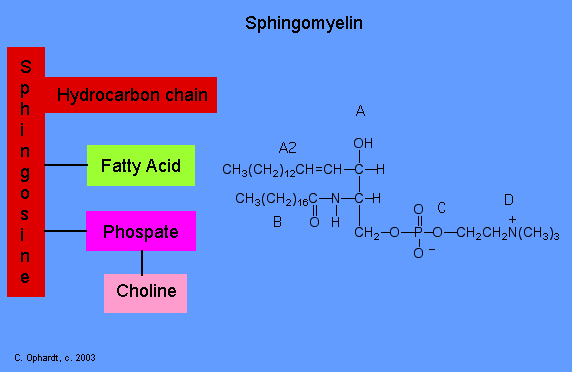
Sphingolipids
Sphingolipids are based on sphingosine rather than glycerol. Sphingomyelin is a typical example.
Sterols
Sterols have a tetracyclic hydrocarbon ring system with an attached hydrocarbon chain. Cholesterol is a typical example.

Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin A (retinol) is a typical example.
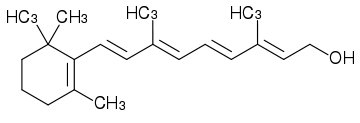
The OH group is the polar head of the molecule.



