Question #424e1
1 Answer
Explanation:
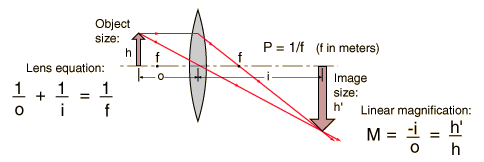
As image formed by the lens is real it follows that lens is convex.
Let object be located at a distance
We know for that for a thin lens of focal length
#1/v+1/u=1/f#
Keeping in view the sign convention the object distance is
When another lens is added to it, the image shifts
From lens' formula we know that focal length
Also from lens equation we get
Now from equations (2) & (3), we get
Subtracting (1) from (4)
Thus Power P of second lens
