What is the natural transmutation which forms most of the argon in air?
1 Answer
Potassium-40 decays to argon-40 via electron capture.
Explanation:
Potassium-40,
Electron capture takes place when an electron from the inner shells of an atom is captured by the nucleus. The negatively charged electron will combine with a proton, which is a positively charged particle, to form a neutron.
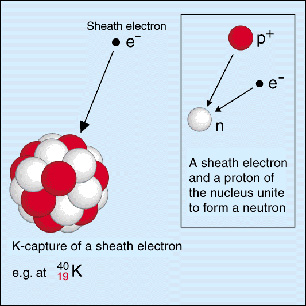
In addition to this, an electron neutrino,
So, if a proton is being converted to a neutron, it follows that the identity of the atom will change. More specifically, its atomic number will decrease by
Its mass number, which tells you the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, will remain unchanged.
The nuclear equation for the electron capture decay of potassium-40 to argon-40 looks like this
#""_19^40"K" + ""_text(-1)^0"e"^(-) -> ""_18^40"Ar" + nu_e#
About one in nine potassium-40 atoms decays to argon-40, the rest decay to calcium-40 via beta minus decay.

