Which of the following species has a higher nucleophilicity in hydroxylic solvents: #CH_3CO_2^-#, #CH_3S^-#, #HO^-#, #H_2O#?
1 Answer
Explanation:
The key factors that affect the strength of the above nucleophiles are charge, resonance. electronegativity, and atomic size.
Charge
Nucleophilicity increases as the density of negative charge increases.
An anion is always a better nucleophile than the corresponding neutral molecule.
Thus, we can drop water from the list.
Resonance
Of the three species with a negative charge, the electrons of acetate ion are delocalized by resonance.
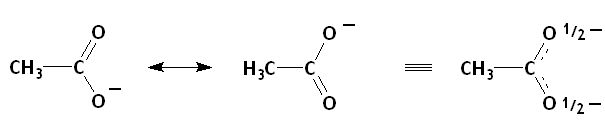
(from en.wikibooks.org)
The charge density on each oxygen atom is decreased, so acetate ion is not a strong nucleophile.
Electronegativity
A highly electronegative atom is a poor nucleophile because it is unwilling to share its electrons.
Furthermore, in a protic solvent, an ion like
This hinders its ability to attack the substrate, so its nucleophilicity decreases.
Atomic Size
- An
#"S"# atom is less electronegative than#"O"# , so it is more willing to share its electrons. - The larger electron cloud about the
#"S"# atom is more polarizable, so it can start bonding from a greater distance from the substrate. - The charge density in the larger electron cloud does not attract a protic solvent shell as strongly in a smaller electron cloud.
These three factors make

