Make the internet a better place to learn
How do oceans absorb CO2?
Answer:
1) Differences in pressure between the air and the ocean cause carbon dioxide to be exchanged and 2) algae and phytoplankton absorb carbon dioxide.
Explanation:
The ocean can absorb carbon dioxide (
 )
)
Carbon dioxide moves between the atmosphere and the ocean by molecular diffusion: a difference between
The solubility of carbon dioxide varies based on salinity and temperature of the water and there is a finite amount that the water can absorb. The colder the water, the more
The solubility of
Another way in which the ocean absorbs
For more information:
What is the best way to deal with those preaching climate change denial or questions asked about the validity or debate of climate change?

Answer:
With patience and maturity.
Explanation:
As Socratic has recently launched the environmental science section, we seem to have an influx of questions along the lines of, "Is climate change real," "What proof is there of climate change," "How can we be sure these aren't natural variations," and so forth. Thus, I think it's a good idea to brainstorm how to best tackle these situations.
For starters, many of these questions are essentially duplicates of one another and you can always mark a question as a duplicate.
In extreme cases, you can also mark a question as inappropriate.
That said, I'd like to remind everyone here that the main mission of Socratic is to teach: to make concepts accessible, to make learning easier, to break concepts down into simpler parts so that learning can occur. That said, reading comments/answers/questions in which people are actively spreading false information or posing questions asking how climate change can be true is certainly frustrating. We've all been there. Don't fight fire with fire though, so to speak. Rather than getting angry, respond clearly and don't get personal.
Ask yourself what are the best facts we have that climate change is caused by humans and is happening? Then ask yourself, how can I clearly communicate those facts? I'd advise against listing ten pieces of evidence. I'd also advise against just providing a link to other websites. Instead, pick a few key pieces of evidence and explain them yourself. Use images, videos, graphs, links to other Socratic concepts, and your words to teach. Remember your basics.
Remember, many people just haven't been taught enough about the science behind climate change or they haven't been taught the concepts well. Hopefully you joined Socratic to help others learn, so try and have some patience and explain these concepts in a way that makes climate change science more accessible and less confusing.
In some cases, a person's religious beliefs conflict with climate change, and this is a really hard situation to handle. Be careful and be considerate of other people's beliefs while maintaining the science behind climate change.
Why do some people say global warming is real and others say it is not?

Answer:
There are varying reasons.
Explanation:
There are multiple reasons why some people do not believe in global warming or climate change (to understand the difference and why the latter term is preferred, see this answer.
When you look at the people who actually study climate science and are actively publishing their results, 97% of them agree that climate change is caused by humans. Thus, those who "believe" in climate change may understand the science or may follow enough science to have repeatedly heard that climate change is real. Higher education in the US frequently gives students the opportunity to take classes either on climate change directly or that include climate change as part of the course. Thus, some young adults are exposed to the science through their education, and in some schools climate change may be taught as part of the K-12 education.
The main reasons people do not believe in climate change are:
- Those contributing to climate change are invested in convincing the public that climate change is a controversial topic or that it is false
- The media misrepresents climate change
- Scientists are often poor at communicating climate change science to the public
- In some parts of the U.S., there are cultural factors that collide with climate change
One of the less well-known reasons why many people do not believe in climate change is that there is an active campaign to distribute misinformation and create doubt surrounding the science. A very good movie/book worth looking into on this subject is Merchants of Doubt. Those who would benefit from climate change being false (fossil fuel companies for example) have reasons to spread false information.
The Heartland Institute is a powerful think tank in the US that does a brilliant job of creating fake science that looks like real science in varying forms. There's a good article about their work here.
Another problem is that many scientists do not do a good job in communicating their research to the public. Often they use jargon and do not represent themselves well when communicating with or through the media. By presenting themselves and their work in an manner that is inaccessible to most people, scientists can create more confusion about climate change and they may also cause people to stray away from reading about science.
The media also plays a critical role in why people do not believe in climate change. The media likes to portray climate change as an unresolved debate. They will put a climate scientist against a politician or someone who does not believe. However, this makes it seem as though the number of believers vs nonbelievers in science is equal. It's not. You may remember a petition where supposedly 30,000 scientists who have a problem with climate change. If you look at those names, very few are climate scientists and some of the names are even fake.
Mainstream media in the US is frequently inaccurate when reporting on climate change. They often get the science wrong or miss seemingly small but important details. A recent report found 72% of Fox News' reporting on climate change contain misleading statements.
Another reason why climate change is so controversial in the United States has to do with certain cultures and the authority that those cultures have. There are some who believe that god wouldn't allow such severe climatic catastrophes that are in our future, thus climate change must be false. There are those who believe scientists are corrupt and do not understand the process of science or the extensive review process it entails. There is a well-written article about this topic here.
Dr. Katharine Hayhoe has done some excellent work on science communication, religion, and climate change and has written a book on the topic.
What is the water cycle?

Answer:
The water cycle describes the movement of water on earth.
Explanation:
The water cycle describes the movement of water on earth. This movement can occur on the surface of the planet, below the surface of the earth, and in the atmosphere. The water cycle includes water in many forms (rain, ice, water vapor, etc.). The water cycle is always moving, although some changes occur quickly other changes may take millions of years.
 )
)
The water cycle describes changes as water moves from one reservoir (such as the ocean, a lake, or an aquifer) to another. This cycle is powered by the sun, which provides needed energy.
Water evaporates from the oceans, freshwater sources, soils, and etc and absorbs energy. It releases energy during the process of condensation and precipitation. When You can watch a short animation of a water drop moving through the water cycle here.
The USGS has an excellent interactive site on the water cycle that can be found here.
See this same question answered in Earth Sciences and check out these related questions on phase changes and the water cycle and how human activities affect the water cycle.
How are niches and habitats different?

Answer:
A niche includes a species' habitat but a habitat does not include a species' niche.
Explanation:
A habitat is the geographical area a species lives in. Examples include the Greater Hinggan pine forest in China, the Arctic tundra, the Amazon rainforest, the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, and so forth.
A niche is defined as the role and position an organism has within its environment. Thus, a niche would include the habitat but a description of an organism's niche would also include position in the food chain, how the organism alters the habitat, and what effect the organism has on other organisms (what does it eat, what other species does it compete with, and so forth).
Many animals may have the same habitat, but they will have different niches.
Each of the finches below may occupy the same exact habitat. Consuming different food items is one factor that contributes to each species having its own unique niche.
 )
)
What might replace fossil fuels in the future?

Answer:
This is a question that scientists and engineers are thinking a lot about and are undecided.
Explanation:
Fossil fuels provide the majority of the planet's energy, thus it is going to take a lot work to replace fossil fuels with more environmentally friendly energy sources.
A combination of renewable energy technologies may replace fossil fuels. For example, wind farms, nuclear energy, solar energy, hydrogen fuels, biofuels such as algae, and others.
 )
)
It will likely take a combination of these technologies to replace fossil fuels, and different areas will likely use different combinations. It's also worth considering that, as more people use these technologies, more money will be invested in them, and more research can be done on improving these technologies even further.
Some countries are choosing to invest their time and money into renewable energy sources:
 )
)
Reducing our energy use overall though would help us rely on renewable energy. We can do this by creating better public transportation, eating foods that are local and in season, creating usable bike lanes in cities, using less energy at home and using energy efficient appliances, and so forth.
To read more about what is possible when it comes to renewable energy, check out this article.
Why are fossil fuels harmful for the environment?

Answer:
Fossil fuels are harmful for the environment for a few reasons.
Explanation:
Fossil fuels are harmful for the environment for a few reasons.
The main reason why fossil fuels cause so much damage is due to the amount of carbon dioxide or CO2 emitted when fossil fuels are burned. This burning and release of CO2 is a huge contributor to the greenhouse effect and climate change. More CO2 in our atmosphere causes less sunlight to escape back into space, causing the planet to warm.
When fossil fuels are burned, CO2 isn't the only gas released. Other harmful gases such as nitrogen and sulfur oxides. Burning fossil fuels causes air pollution and smog.
Acid rain is also caused by the burning of fossil fuels. While technology has improved considerably in the US, we used to see high instances of acid rain around industrial areas where lots of fossil fuels were being burned. This is still the case in areas where air quality is not as regulated.
Another reason why fossil fuels are bad for the environment has to do with the ways they are extracted or removed from the earth. Drilling and mining for coal, natural gas, and oil all involve disrupting the natural landscape to access these materials. Drilling can disrupt the water table and if spills or accidents occur, we can have incidents like the Deepwater Horizon Spill.
An example of a coal mine:

Extent of Deepwater Horizon Spill:
 )
)
To read more about this issue, check out this article on the hidden cost of fossil fuels.
How do greenhouse gases trap heat?
Answer:
It all has to do with the wavelength.
Explanation:
Electromagnetic radiation travels in waves, and the distance from one wave crest to the next is known as the wave length.
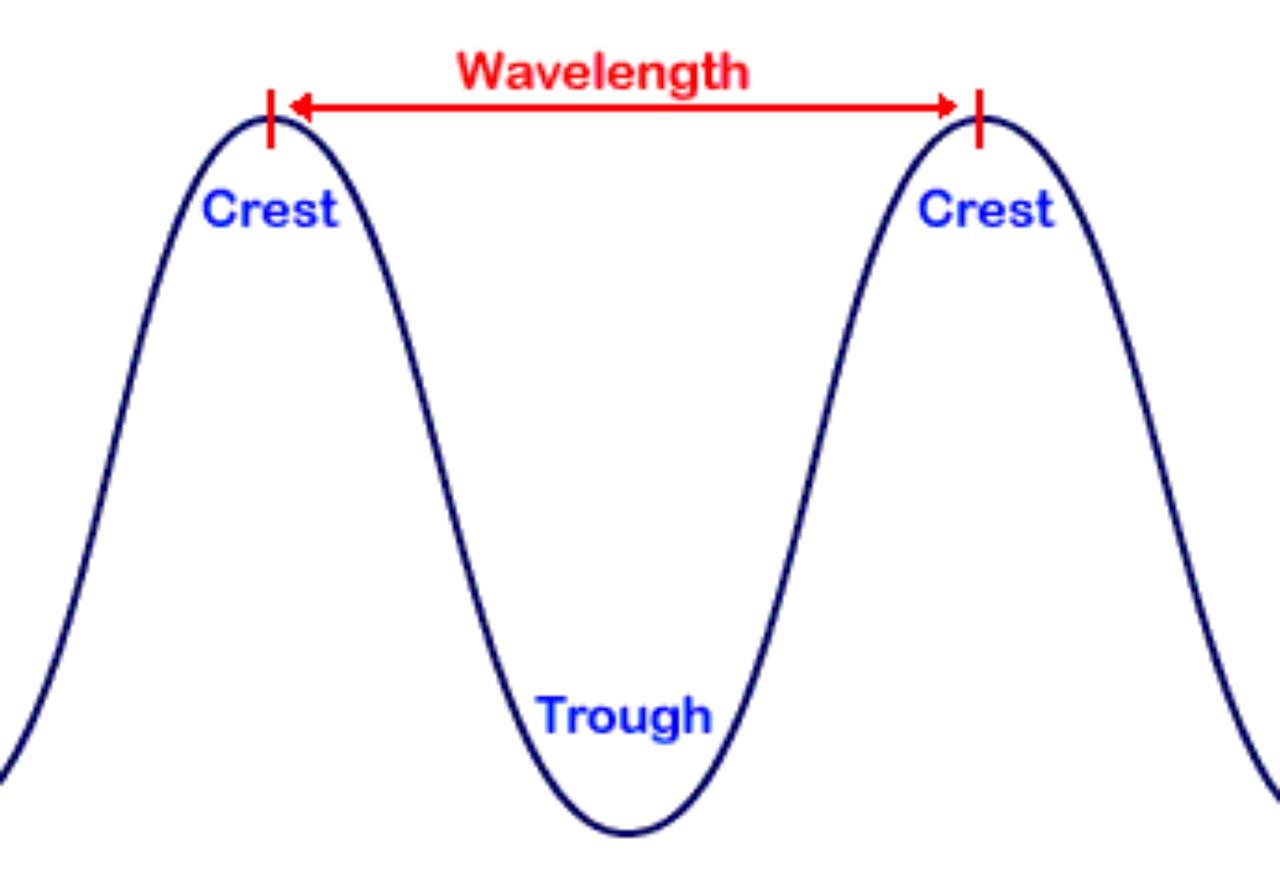
Generally speaking when these wave encounter something they will either through it or be blocked by it. A general rule of thumb is the smaller the wavelength the more likely it will pass through the material.
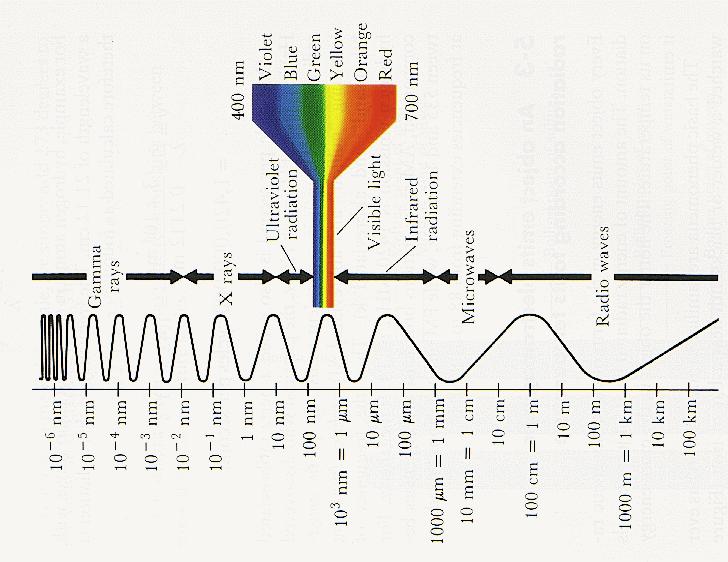
In the illustration above you can see the smaller wavelengths are things like x rays and gamma rays. If you have had to have an x-ray you know that x-rays travel freely through a lot of material (such as your skin). The calcium of your bones will block some x-rays (which is why they appear on the xray film), but the reason that you wear lead everywhere that you do not need x-rayed is that it takes lead to fully stop x-rays. Gamma rays are even harder to block, and need a much thicker lead shield.
What does this have to do with greenhouse gases?
Well you see on the picture above the area that is a rainbow? That is where most of the radiation from the sun falls, and we call it visible light. Energy at this wavelength passes freely through the atmosphere, and can strike the Earth. When it strikes the Earth the energy is absorbed and the Earth is heated. Heat is actually another form of electromagnetic radiation called infrared radiation. What is crucial to note is that this type of radiation has a longer wavelength.
Greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, etc.) are transparent to visible light, but opaque to infrared radiation. That means the sunlight travels through them but the heat is blocked by them. That is how greenhouse gases trap heat.
Side note, we call heat infrared radiation because it is adjacent to the red end of the visible light spectrum. We call the radiation adjacent to the other side of the visible light spectrum Ultraviolet radiation, because it is adjacent the the violet end of the visible light.
Additional side note, the sun actually emits radiation over a wider spectrum than just the visible light spectrum.
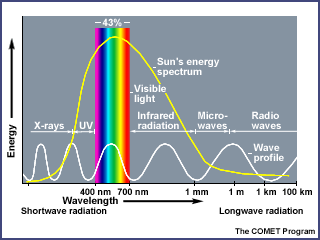
The Ultraviolet part of the solar energy is blocked by ozone in the upper atmosphere (which is why we need the ozone layer). The infrared radiation of the inbound solar radiation is also blocked from entering by greenhouse gases.
How do biomes differ from ecosystems?

Answer:
Explanation:
An example of an ecosystem is a pond. All of the living things in the pond (frogs, fish, bacteria, water plants etc.) are considered biotic factors . The abiotic factors of the pond ecosytem would include all of the non-living factors (water, light, dissolved oxygen, nitrates etc.) which are found in the pond.
A biome is a collection of different ecosystem that share similar climate conditions. Northeastern Minnesota is coniferous forest biome. In this region of the state of Minnesota you will find pond ecosystems, forest, rivers & streams etc.
This video discusses levels of organization in ecology, including discussion of ecosystems and biomes.
Hope this helps!
What is the role of greenhouse gases in global warming?
Answer:
They prevent heat from escaping.
Explanation:
Electromagnetic radiation travels in waves, and the distance from one wave crest to the next is known as the wave length.

Generally speaking when these wave encounter something they will either through it or be blocked by it. A general rule of thumb is the smaller the wavelength the more likely it will pass through the material.

In the illustration above you can see the smaller wavelengths are things like x rays and gamma rays. If you have had to have an x-ray you know that x-rays travel freely through a lot of material (such as your skin). The calcium of your bones will block some x-rays (which is why they appear on the xray film), but the reason that you wear lead everywhere that you do not need x-rayed is that it takes lead to fully stop x-rays. Gamma rays are even harder to block, and need a much thicker lead shield.
What does this have to do with greenhouse gases?
Well you see on the picture above the area that is a rainbow? That is where most of the radiation from the sun falls, and we call it visible light. Energy at this wavelength passes freely through the atmosphere, and can strike the Earth. When it strikes the Earth the energy is absorbed and the Earth is heated. Heat is actually another form of electromagnetic radiation called infrared radiation. What is crucial to note is that this type of radiation has a longer wavelength.
Greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, etc.) are transparent to visible light, but opaque to infrared radiation. That means the sunlight travels through them but the heat is blocked by them.
All this is actually natural and is part of the energy budget of the Earth.
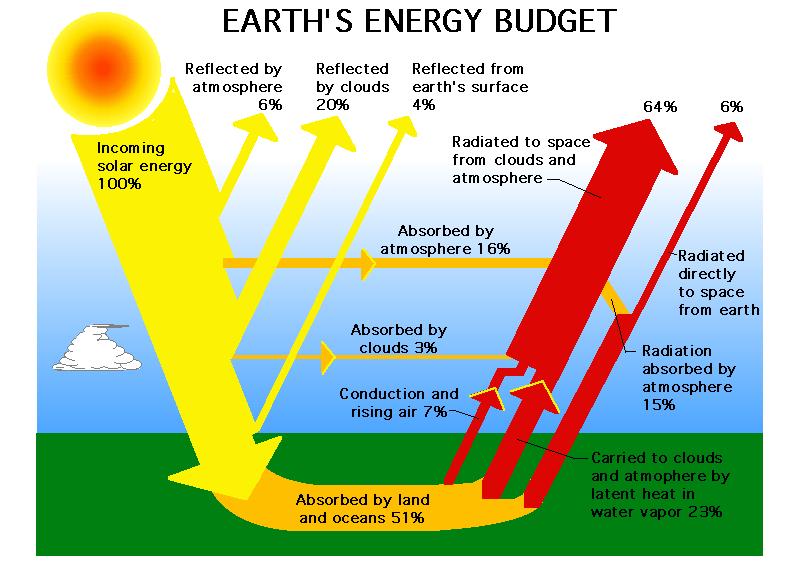
If you look at the diagram above you see that a certain amount of heat is supposed to be blocked by greenhouse gases. The problem is when greenhouse gases increase and block more heat than they are supposed to. This causes the temperature of the Earth to increase so that the amount of heat the Earth releases can increase and the budget can get back in balance.